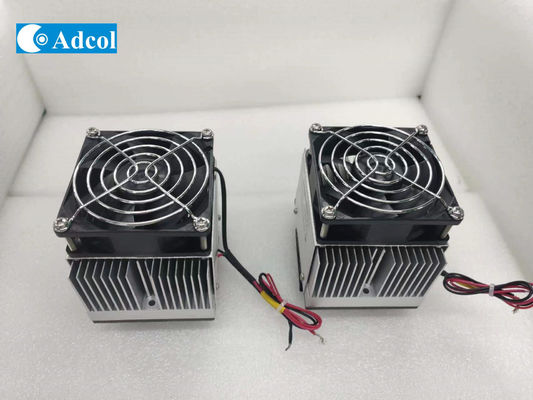
39 Watt Peltier Plate Cooler Electrical Cooling Plate 4A Stable Current
Overview
• The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice-versa.
–A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when a temperature difference is applied to it.
–Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, it creates a temperature difference.
Why Use TE ?
• Pros:
–Unlike common heat pumps (compression/expansion-based and Stirling cycle), these devices have no moving parts and work in any orientation
• simple, reliable, compact, low mass, and noiseless, vibration-less operation.
–Less maintenance - more than 100,000 hours of life for steady state operation
–Function in environments that are too severe, too sensitive, or too small for conventional refrigeration
–Contains no chlorofluorocarbons or other materials which may require periodic replenishment
• Temperature control to within fractions of a degree using appropriate support circuitry.
–Low thermal mass and fast response time of TECs, when combined with an appropriate control loop, can provide precise temperature control. In relatively stable thermal sink environments, TECs achieve 0.01°C temperature stability. Such extreme stability is difficult to achieve by other means.
–The direction of heat-pumping is fully reversible. Changing the polarity of the DC power supply causes heat to be pumped in the opposite direction, i.e.- a cooler can become a heater.
–Temperature differences:
• for a hot side around room temperature, temperature differences of about 72°C and 125°C can be achieved by single-stage and multistage TECs, respectively.
• In situations where the object being cooled generates little or no heat the combination of TE cooling and thermal insulation can produce large temperature differences.
•
• Cons:
–structural integrity of bismuth telluride and soldered joints when subjected to differential thermal expansion stresses.
–relatively low COP, particularly with large temperature differences.
• this can be acceptable when the heat load is small.
• best suited to situations with modest heat loads, cold temperatures not below 150°K, and hot-to-cold-side differences not exceeding 100°C.
• not recommended for use below 130°K because of their prohibitively low efficiencies.
| Air to Plate Item# |
ATP040-12VDC |
| Cooling Capacity(W) |
39 |
| Current(A) |
4 |
| Voltage(VDC) |
12 |
| Weight(kg) |
0.8 |
Dimension (mm)
(Cold side) |
Length |
60 |
| Width |
40 |
| Height |
10 |
Dimension (mm)
(Hot side) |
Length |
120 |
| Width |
102 |
| Height |
59 |


 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 





